Founder’s Insights | Vertically Oriented Smaller Generative AI Models will Produce Early Winners in the Current AI Race

Introduction
A new paradigm is emerging in the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence (AI): smaller, vertically-oriented generative AI models. This approach departs from the traditional, horizontally-oriented models that aim to solve many problems. Instead, it develops specialized AI models to solve problems within a particular industry, or vertical. Vertically-oriented Generative AI models cater to specific industries, offering improved accuracy, enhanced performance, and increased efficiency. These models address a specific industry's unique needs and challenges. I will focus on why vertically-oriented smaller generative AI models are beneficial in mining, and how the industry can use them.
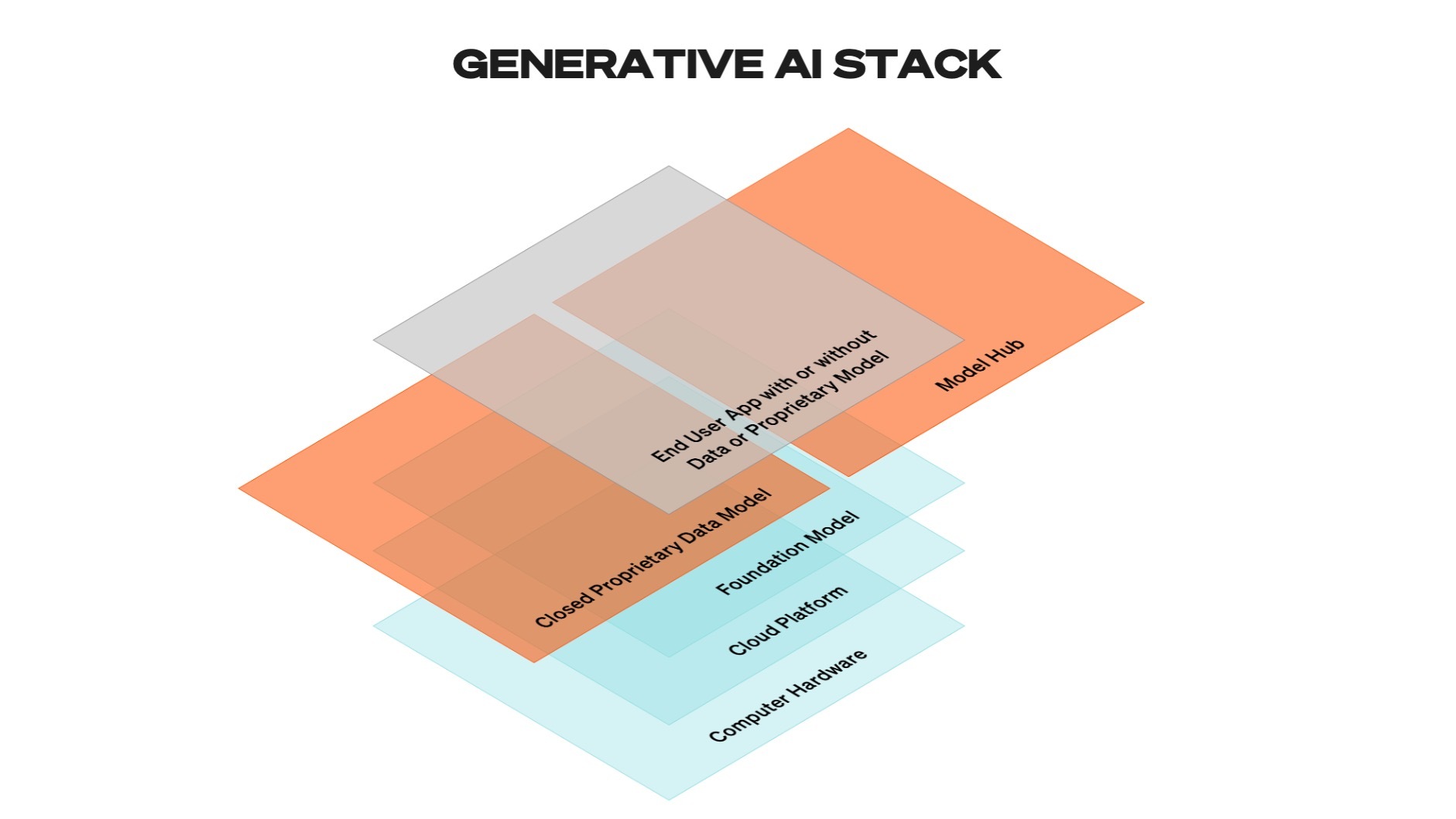
GENERATIVE AI PLATFORM (GaP)
At the heart of this new paradigm is the concept of what I call a Generative AI Platform (GaP). A GaP is a foundational AI model designed to improve continuously over time. Like other sophisticated AI models, as new data becomes available and AI research advances, the GaP evolves, becoming more accurate, efficient, and capable. This continuous improvement allows the GaP to adapt to changing conditions and requirements, ensuring it remains relevant and effective.
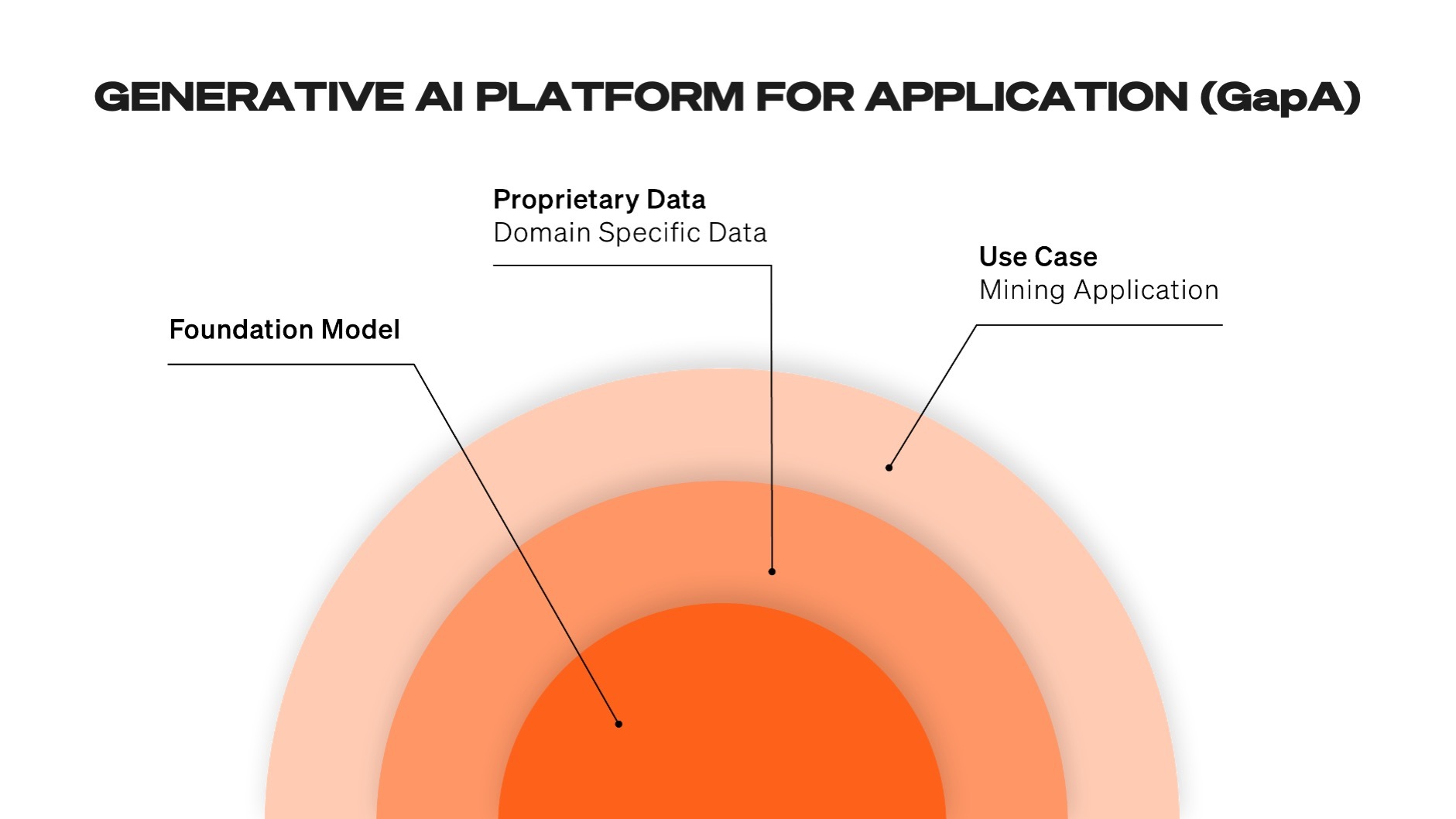
GENERATIVE AI PLATFORM FOR APPLICATION (GapA)
Building on the GaP is what I call the Generative AI Platform for Application (GaPA). The GaPA takes the foundational GaP and fine-tunes it with proprietary and domain-specific data. This could include data specific to the industry and generated through human interaction with the model. The fine-tuning process allows the GaPA to become highly specialized, enabling it to solve specific problems.
Take customer service as an example. Many companies use AI-powered tools to manage customer questions and concerns—but the range of inquiries is vast, and the model can’t be prepared for everything. With the GaPA, the model can learn from each interaction to be better for next time. So while it may be stumped the first time a customer asks how many outlets their hotel room has, it will be prepared the next time.
The GaPA is not just about creating a specialized AI model, though. It's also about choosing the right application and workflow to leverage the GaP's output. By aligning the AI model with the right application, achieving measurable ROI is possible. This is a key advantage of the vertically oriented approach: focusing on specific problems and applications makes seeing results faster is possible.
Propelling the Mining Industry Ahead: The Mining Industry as a Case Study
With its complex operations and vast data sets, the mining industry presents an ideal case study for applying vertically oriented smaller generative AI models. Mining operations generate a wealth of data, from geological surveys and drilling reports to equipment telemetry and environmental impact assessments. This data is incredibly valuable, but it's also complex and difficult to analyze.
By embracing smaller, vertically-oriented Generative AI models, mining companies can position themselves as early winners in the AI race. These models empower organizations to tailor AI solutions precisely to their mining-specific needs, granting them a competitive advantage in efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and innovation. By leveraging Generative AI's capabilities, mining companies can optimize exploration efforts, streamline production processes, deliver superior products, demonstrate sustainable practices, and gain a significant edge in the market.
Traditional, horizontally-oriented AI models struggle to make sense of this data because they're not designed to handle the specific challenges and nuances of the mining industry. This is where a Generative AI Platform for Application (GapA) comes into play. By fine-tuning a foundational Generative AI Platform (GaP) with mining-specific data, it's possible to create an AI model that understands the intricacies of mining operations. The mining industry is data-rich and complex, with specific problems that AI models are well-suited to address and help solve. Companies that embrace and effectively implement Generative AI Platforms for Application (GapA) now have a unique opportunity to emerge as industry leaders.
But creating a specialized AI model is only half the battle. To achieve measurable ROI quickly, picking the right application and workflow is crucial. Here are just a few examples:
- Analyze combined remote sensing, geological sampling and geotechnical datasets simulating the distribution of mineral deposits for optimized targeting, resource estimation and extraction.
- Integrate mining operations with environmental and processing parameters to better control reagents, grade, and impurities to improve community and processing outcomes.
- Dynamically adjust parameters based on local grid energy balance and renewable energy profile as mines move to 100% electric and autonomous.
- Identify patterns affecting the inherent safety hazards for the labor force and allow companies to adopt preemptive controls.
- Apply it to their drilling operations, where it can help optimize drilling patterns to reduce waste, costs and environmental impact.
- Apply it to their maintenance operations, where it can predict equipment failures before they happen and to schedule preventive maintenance.
To date, Generative AI applications haven't been broadly discussed in heavy industry, but mining actually has a massive opportunity to capitalize on these technologies. Unlike the publicly available internet datasets that have trained the foundational models, the data in heavy industry operations is proprietary and private. This means that mining companies—especially industry incumbents—have exclusive access to a wealth of industry-specific data that can be used to fine-tune a GaP into a highly specialized GapA. By leveraging this unique data, mining companies can develop AI models that are specifically tailored to their operations. By taking the initiative to apply Generative AI in their operations, mining companies can benefit from Generative AI today. This not only provides a competitive advantage, but also sets a benchmark for other peer companies. It sends a clear message to the market: real-world problems in heavy industries can be solved effectively and efficiently with the right AI strategy.
Conclusion
Heavy industries, by their very nature, tend to be conservative in their approach to adopting new technologies. This is particularly true when it comes to emerging technologies like Generative AI, where the benefits and risks are still being understood. As such, it's likely that most heavy industry companies may be reluctant early adopters of Generative AI.
However, incumbent construction and mining companies have an innate advantage in this space. They possess unique, proprietary data that can be used to fine-tune generative AI models to their specific needs. This gives them the potential to lead the market in the application of these models, despite their conservative nature. Taking the first step towards adopting generative AI now is not just about gaining a competitive advantage in the present. It's also about laying the groundwork for future growth. By starting to explore and implement Generative AI now, companies can learn, adapt, and evolve along with the technology. This will position them well to leverage the full power of Generative AI as it matures.
In my next post, I will discuss how companies can develop an in-house AI strategy to guide their adoption of Generative AI. This strategy will help companies navigate the challenges and opportunities of Generative AI, ensuring they are well-prepared to seize the benefits this technology offers.
While the adoption of Generative AI in heavy industries may be slow to start, the potential benefits are significant. By taking the lead in this area, mining and construction companies have the opportunity to not only solve their most pressing problems but take advantage of Generative AI today.
Special thanks to Shane Clark, Head of Growth & Sustainability at Thiess for his thoughts and important contributions to this article.
You can follow Bibhrajit on LinkedIn and Twitter to stay informed about the latest advancements in AI and learn how heavy industry can leverage its transformative potential.
